

The world is shrinking and leaders from different cultures are finding that they need to work together. The cultures are formed of geography, faith, gender, generation, organization and sector. And in a global world, where problems cross borders between cultures, we need leaders who can cross those boundaries and cross cultures too; people who can communicate effectively and build diverse networks necessary to solve messy problems. We need leaders who don't just shy away from difference but gravitate towards it. They don't see heterogeneity as threatening; they see it as creative, exciting, inspiring and enriching.
Cultural intelligence, also known within business as "cultural quotient" or "CQ", is a theory within management and organisational psychology, positing that understanding the impact of an individual's cultural background on their behaviour is essential for effective business, and measuring an individual's ability to engage successfully in any environment or social setting. CQ teaches strategies to improve cultural perception in order to distinguish behaviours driven by culture from those specific to an individual, suggesting that allowing knowledge and appreciation of the difference to guide responses results in better business practice.
The term "culture" is often used as a synonym for nationality or ethnicity. However, it can also apply to different ideological or political groups, and to different organizations, age groups, or departments.
Cultural intelligence or CQ is measured on a scale, similar to that used to measure an individual's intelligence quotient. People with higher CQs are regarded as better able to successfully blend into any environment, using more effective business practices, than those with a lower CQ.
In culturally diverse business situations, CQ predicts the following:
- Personal Adjustment and Adaptability
- Judgment and Decision Making
- Negotiation Effectiveness
- Trust, Idea Sharing, and Innovation
- Leadership Effectiveness
- Profitability and Cost-Savings
CQ is developed through:
1. cognitive means: the head (learning about your own and other cultures, and cultural diversity)
2. physical means: the body (using your senses and adapting your movements and body language to blend in)
3. motivational means: the emotions (gaining rewards and strength from acceptance and success)
There are four CQ capabilities:
1. motivation (CQ Drive),
2. cognition (CQ Knowledge),
3. meta-cognition (CQ Strategy) and
4. behavior (CQ Action).
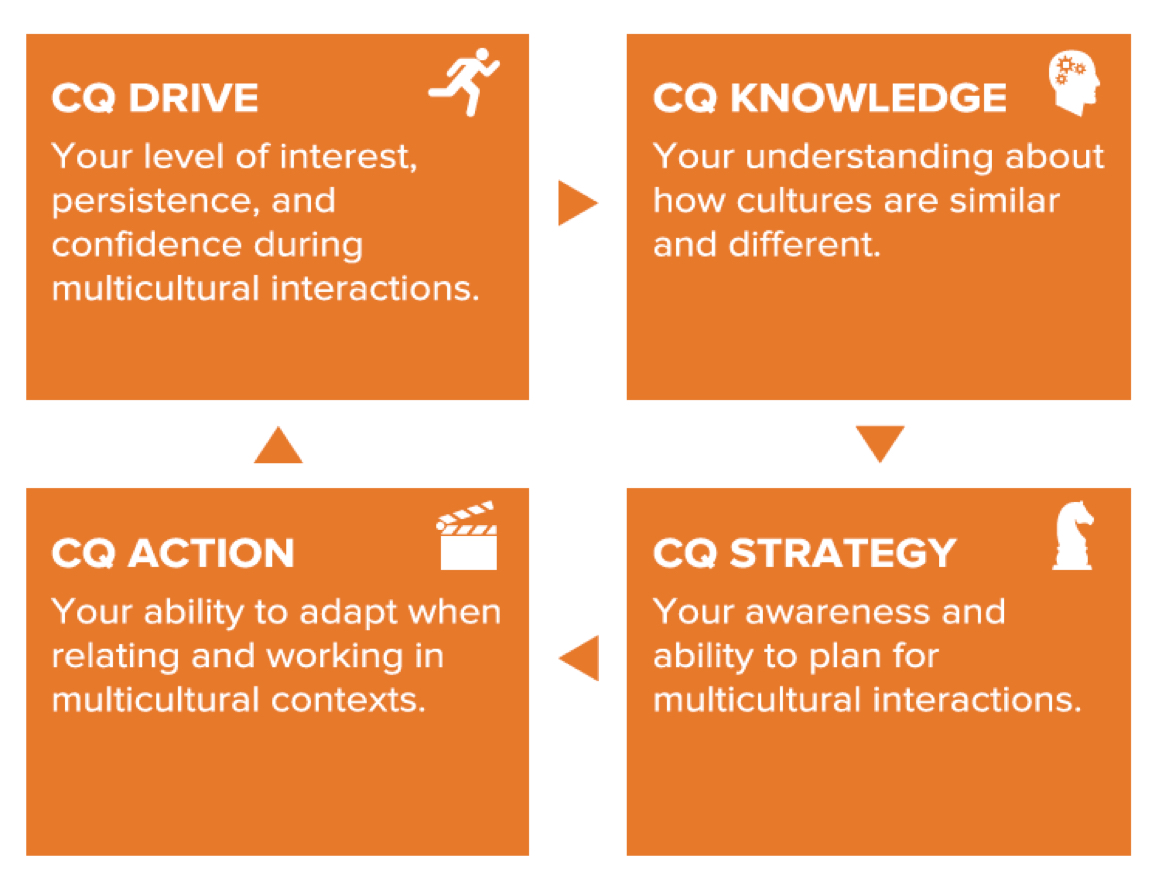
CQ Assessments report scores on all four capabilities as well as several sub-dimensions for each capability. The four capabilities stem from the intelligence-based approach to intercultural adjustment and performance.
1. CQ-Drive: CQ-Drive is a person's interest and confidence in functioning effectively in culturally diverse settings. It includes:
- Intrinsic interest - deriving enjoyment from culturally diverse experiences
- Extrinsic interest - gaining benefits from culturally diverse experiences
- Self-efficacy - having the confidence to be effective in culturally diverse situations
2. CQ-Knowledge: CQ-Knowledge is a person's knowledge about how cultures are similar and how cultures are different. It includes:
- Business - knowledge about economic and legal systems
- Interpersonal - knowledge about values, social interaction norms, and religious beliefs
- Socio-linguistics - knowledge about rules of languages and rules for expressing non-verbal behaviors
3. CQ-Strategy: CQ-Strategy is how a person makes sense of culturally diverse experiences. It occurs when people make judgments about their own thought processes and those of others. It includes:
- Awareness - knowing about one's existing cultural knowledge;
- Planning - strategizing before a culturally diverse encounter;
- Checking - checking assumptions and adjusting mental maps when actual experiences differ from expectations.
4. CQ-Action: CQ-Action is a person's capability to adapt verbal and nonverbal behavior to make it appropriate to diverse cultures. It involves having a flexible repertoire of behavioral responses that suit a variety of situations. It includes:
- Non-verbal - modifying non-verbal behaviors (e.g., gestures, facial expressions)
- Verbal - modifying verbal behaviors (e.g., accent, tone)
Additional research on cultural intelligence is being conducted by academics around the globe, including research on culturally intelligent organizations, the correlation between neuroscience and the development of cultural intelligence, and situational judgment making and CQ Assessment.
Benefits of CQ for businesses:
- Success in culturally diverse markets
- Speed and efficiency when working across borders
- Effective short-term and long-term global assignments
- Becoming an employer of choice
- Profitability and cost savings
- Multicultural team effectiveness
- Global virtual team effectiveness
People with high cultural intelligence are not experts in every culture; rather, they use observation, empathy, and intelligence to read people and situations, and to make informed decisions about why others are acting as they are. They also use cultural intelligence to monitor their own actions. Instead of making quick judgments or relying on stereotypes, they observe what is happening, and they adapt their own behavior accordingly.
CQ Workshop Outline:
- The business case for cultural diversity
- Challenges managing cultural diversity
- The nature and origin of cultural bias
- Cultural diversity and inclusion in Australian workplaces
- Moving from colour blind to colour brave
- Understanding culture and its implications for interpersonal relations
- Self-awareness: Understanding your orientation in ten main cultural dimensions
- Other-awareness: Mapping cultural dimensions to cultural clusters
- The cultural intelligence (CQ) model
- Developing the four main CQ competencies
- Mapping cultural differences to work preferences (e.g. feedback, influencing, decision-making, trust, teaming, conflict resolution)
- Applying CQ for cultural inclusion, including best practices for managing multicultural teams
- Personalised development plan
Learning Outcomes
- Increased awareness of the role of culture in interactions
- Know-how to improve cultural intelligence in self and others
- Improved effectiveness working with diverse colleagues, customers, suppliers and other stakeholders
- Inclusive mindset and expansive worldview
- Personal growth
- Enhanced adjustment and well-being


